Over 2 million + professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Unlock the essentials of corporate finance with our free resources and get an exclusive sneak peek at the first chapter of each course. Start Free
The monetary transmission mechanism refers to the process through which monetary policy decisions affect economic growth, prices, and other aspects of the economy.
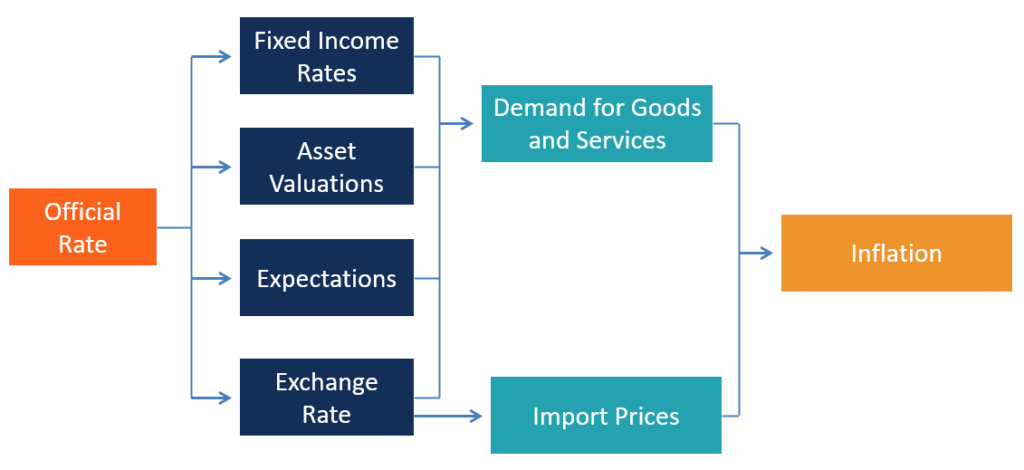
The chart below illustrates a simplified monetary transmission mechanism, which will be further analyzed in this article.

Central banks throughout the world share similar objectives. The predominant objective of central banks is price stability, but low unemployment and sustained economic growth are often important objectives as well.
To reach their goals, central banks can count on several monetary policy tools, such as interest rates, quantitative easing/tightening, reserve requirements, and interest on reserves.
The effects of monetary policy on the economy may not be obvious, especially if the principle of money neutrality is accepted. However, the actions of central banks to try to affect the economy suggest that central bankers believe that, at least in the short term, monetary policy can affect the economy and not just the levels of inflation.
The official interest rate is the most popular tool through which central banks influence the economy. We are going to analyze the monetary transmission mechanism mainly via the analysis of the official interest rate.
The change in the official interest rate is usually transmitted to the economy via four different but interconnected channels – market rates, expectations, asset prices, and exchange rates.
If central banks raise (lower) the official interest rate, bank lending rates, and bond yields would rise (fall) as a consequence. Central banks try to affect the cost of borrowing for businesses and consumers, mainly via changes in the official interest rate.
Changes in the official interest rates exert a significant effect on the expectations of economic agents. If the official interest rates are lowered, economic agents would expect the amount of lending to increase as a result of lower borrowing costs or asset prices to increase as a result of lower discount rates and expectations of better growth.
Conversely, rising interest rates could negatively affect the expectations, as economic agents may expect the amount of lending to decrease due to the increased borrowing costs and asset prices to decline as a result of higher discount rates and expectations of lower economic growth.
Changes in the official interest rate affect the discount rates used to calculate the present value of cash flows, which are used to estimate the value of securities.
It happens because:
Changes in the official interest rate affect exchange rates, as well. Other conditions held equal, when interest rates in a country rise (decline), investing in that country becomes more (less) attractive.
As a result, the demand for the country’s domestic currency increases (decreases) vs. other currencies.
At least in the short term, the changes in the four channels analyzed affect the demand for goods and services.
As mentioned above, changes in the official interest rates can affect demand via several channels. Changes in demand ultimately affect prices, increasing or decreasing inflation pressures. For example, other conditions being equal, a decline in interest rates would result in an inflationary effect, mainly because:
CFI offers the Commercial Banking & Credit Analyst (CBCA)™ certification program for those looking to take their careers to the next level. To keep learning and developing your knowledge base, please explore the additional relevant resources below:
Become a certified Financial Modeling and Valuation Analyst (FMVA)® by completing CFI’s online financial modeling classes!